Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. While its association with bone health is well-known, emerging research highlights its extensive benefits for physical and mental health, making it an essential nutrient for everyone.
What is Vitamin D?

Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that the body produces when exposed to sunlight. It can also be obtained through certain foods and supplements. Unlike other vitamins, it functions like a hormone, affecting nearly every cell in the body.
Key Benefits of Vitamin D

- Strengthens Bones and Teeth
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, essential for bone density and preventing conditions like osteoporosis and rickets. - Boosts Immune System
It plays a pivotal role in bolstering the immune system, helping the body fend off infections and illnesses. - Supports Mental Health
Low levels of Vitamin D have been linked to depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Maintaining adequate levels may improve emotional well-being. - Reduces Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research suggests that Vitamin D may lower the risk of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. - Improves Muscle Function
Vital for muscle strength, it helps prevent falls and injuries, particularly in older adults.
How to Get Enough Vitamin D
- Sunlight Exposure
The body naturally produces Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Spending 10-30 minutes in the sun several times a week can suffice, depending on skin tone, location, and weather. - Dietary Sources
Include Vitamin D-rich foods such as:- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods (milk, orange juice, cereals)
- Cheese
- Supplements
For individuals who struggle to get enough Vitamin D through sunlight or diet, supplements can be an effective option. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the correct dosage.
The Risks of Deficiency
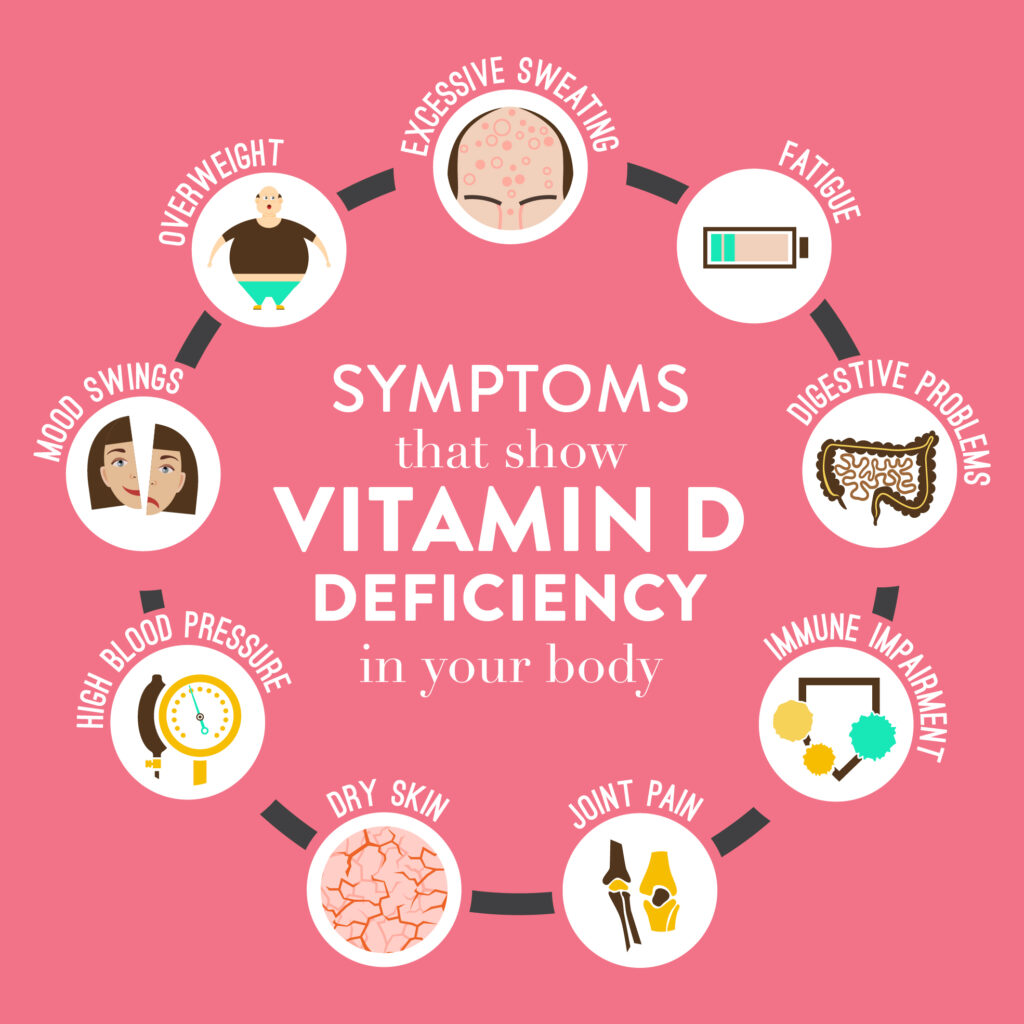
Vitamin D deficiency is common worldwide, especially in individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin tones, or dietary restrictions. Symptoms of deficiency may include:
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Bone pain and muscle weakness
- Depression and mood swings
- Increased susceptibility to infections
Long-term deficiency can lead to severe health problems, including bone deformities in children and osteoporosis in adults.
Can You Have Too Much Vitamin D?

While rare, excessive intake of Vitamin D (usually through supplements) can lead to toxicity, resulting in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, kidney damage, and hypercalcemia. Always adhere to recommended daily intake levels:
- Adults: 600-800 IU per day
- Older adults: 800-1,000 IU per day
Conclusion
![Família feliz na luz do sol do parque. família no fim de semana [download] - Designi](https://www.designi.com.br/images/preview/11059903.jpg)
Vitamin D is a cornerstone of good health, impacting everything from bones to mental well-being. By ensuring sufficient sunlight exposure, incorporating Vitamin D-rich foods, or taking supplements when necessary, individuals can harness the full benefits of this vital nutrient.
Read also:
- Top Foods for Boosting Vitamin D Levels.
- The Link Between Vitamin D and Mental Health.
- How to Recognize and Treat Vitamin D Deficiency.
Stay informed about the latest health tips and trends to lead a healthier, happier life!




